Google is testing laser tech for internet connection in Congo ✽

Brazzaville, the capital city of the Republic of Congo in central Africa is separated from another city called Kinshasa which is the capital city of the democratic republic of Congo by the Congo River flowing in between them.
Google implemented a project called Taara where they expand the global access to affordable and fast internet using beams of light. The main goal was to deliver internet to isolated cities and villages around the world.
What is Taara Project?
Taara uses invisible bean to transmit information at a high speed, this is like fiber but without the cable. The Taara project is relatively new and has been introduced for testing in India and Africa. Although when introduced in India it was not successful as monkeys have climbed on the transmission towers and intercepted the laser beams.
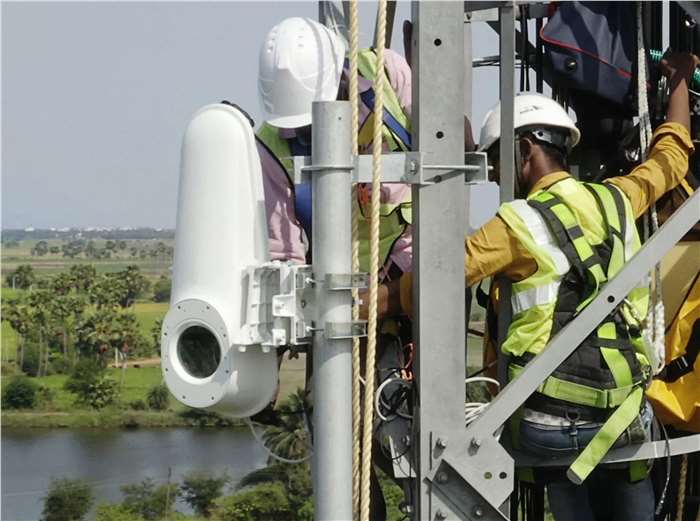
The next pilot testing was done recently between two countries in Africa where the beam transmitted from Brazzaville to Kinshasa through the laser beam. The main reason why this technique was used instead of the traditional cables under river water is because the Congo River is the deepest river in the world with a depth of almost 230 meters below sea level making it almost impossible to connect cables.
The Project improvements
The Taara Equipment were enhanced and modified after its fail in India to withstand almost every weather and climate changes and disasters such as rain, storm, wind, and even birds. The connection would be weak in case of fogs but otherwise expected to survive other harsh environments.
The laser can travel for many kilometers and is supposed to be affordable but due to the cost of the cables that go around the river for 400 kilometers to reach the optic fibers, the cost of the internet in Kinshasa has increased by 5 times.
This project has helped connect two African countries and hopefully in the future more countries could adopt the technique after being perfected to get faster and cheaper internet connections.